


It has become a tradition for Google to release the source code of I/O event Android app after several weeks of the event.
This annual release is done to demonstrate best practices for app development. Developers can take a look at the code to get a better understanding of Google’s best practices for Android App Development.
Google’s I/O 2018 app represents a complete rewrite of the application. The app has moved from ContentProvider+SyncAdapter architecture to Architecture Components.
It’s Google’s Android Team current recommendation for developing modern apps for Android. Google has used Kotlin for the rewrite of the application.
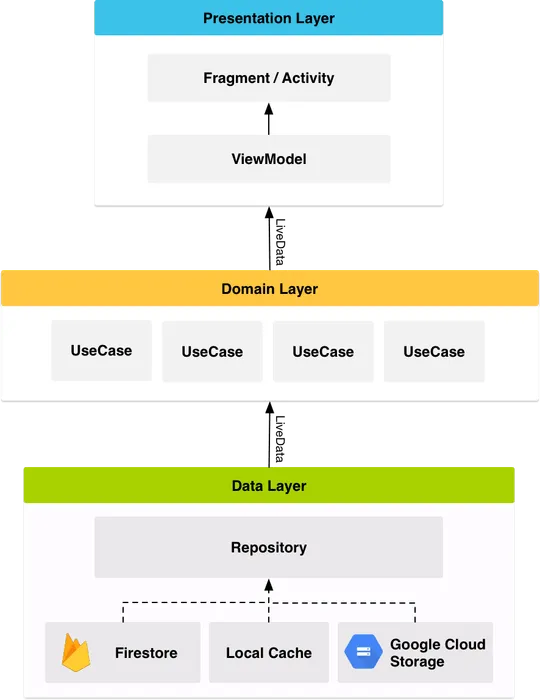
Here is the general overview of the app’s architecture –

Repository layer is used for handling data operations. Data comes from different data sources –
Repository modules are responsible for handling all the data operations.
Dagger2 is used for dependency injection.
Espresso is used for basic instrumentation tests and JUnit and Mockito for unit testing.
The Firebase platform has now matured and the use of Firebase technologies has now increased. Following are the Firebase components used in I/O 2018 –
It is Google’s source for all user data
Firebase Cloud Functions are used to run the backend code. The reservation function, checking user’s status, checking space availability all depends upon on Cloud Functions.
Cloud Messaging is used to inform the app about any sort of changes in conference data using a ping-and-fetch model.
Remote Config is used to inform users about WiFi information, conference schedule, etc in a lightweight manner.
Google made the choice of rewriting the app from scratch in Koltin to bring the modern Android architecture. Using Kotlin for the rewrite is an easy choice because –
At I/O 2018, The Material Design team announced Material Theming which give apps the ability to customize Material Design to bring more personalization of their product’s brand.
As the app was released before Material Theming, so they could not use all of the new components but managed to sneak a few including a new Bottom App Bar with inset Floating Action Button.
The app is available for developers on Github.
App architecture refers to the high-level structure of an application, encompassing the design patterns and methodologies used to organize code and manage data flow. It includes components such as user interfaces, data models, and services, ensuring scalability, maintainability, and efficiency. Good app architecture helps streamline development, improve performance, and facilitate future enhancements.
Kotlin is a modern, expressive, and powerful programming language used by Google for developing Android apps. It offers concise syntax, enhanced functionality, and safety features like nullability and immutability, making it a preferred choice for building robust and maintainable applications.
Firebase is a comprehensive platform offered by Google, providing a suite of backend services for building and scaling mobile and web applications. It offers features such as authentication, real-time database, cloud storage, hosting, and analytics, enabling developers to focus on building great user experiences. With Firebase, developers can quickly develop, deploy, and manage their applications, enhancing productivity and accelerating time-to-market.
Material Theming is a design system introduced by Google that allows developers to customize the visual aspects of their apps while maintaining consistency with the Material Design guidelines. It provides tools and resources for creating unique and branded experiences, empowering developers to tailor their apps’ look and feel to match their brand identity. Material Theming streamlines the design process and ensures a cohesive user experience across different platforms and devices.
Are You Prepared for Digital Transformation?
Mobile App Development
Planning to hire Android developers? This guide covers costs, skills, hiring models, and common mistakes to help you build apps that last.
Healthcare
Building a telehealth app isn’t just coding video calls. It’s about secure, compliant, and user-friendly care platforms. Learn features, costs, and real-world tips to build smarter telemedicine apps.
Devops Consulting
Discover the benefits of DevOps consulting on healthcare mobile apps, from secure and reliable releases to improved compliance and team efficiency